-
Overview
-
Practical sheets
-
-
- Aucun article
-
-
- Aucun article
-
-
-
- Backup : Agent-Level B&R via NSS for IAAS offer
- Backup : Create VCOD Backup
- Backup : Netbackup Agent Installation for Linux
- Backup : Netbackup Agent Installation for Windows
- Backup : Overall Design for VCOD Offer
- Backup : User's Guide for VCOD Offer
- NSX-T : Configuring a Distributed Firewall
- NSX-T : Create VPN Ipsec
- NSX-T : Creation of T1
- NSX-T : DNAT configuration
- NSX-T : How to configure a Gateway Firewall
- NSX-T : SNAT configuration
- NSX-T: Create and Configure a Geneve Overlay Segment
- NSX-T: How to configure an IPSEC solution
- vCenter : Clone a VM
- VCenter : Create a new VM
- VCenter : Create a snapshot of a VM
- VCenter : Reset cloudadmin password
- VCenter : Storage Vmotion on a VM
- VCenter : Upgrade Vmware tools on a VM
-
-
Q & A
-
Services
- Backup
- Bare Metal Server
- Bare Metal Server
- Bare Metal Server GPU
- Block Storage
- BVPN access
- Certifications
- Cross Connect
- Dedicated Cluster
- DRaaS with VCDA
- Dual Site
- Dual Site
- HA Dual-Room
- Internet access
- Licenses
- Loadbalancer As a Service
- Network
- Network Storage
- Object storage
- Object storage
- QoS Appliance
- Security
- Shared colocation switch option (Cross connect)
- Support and Coaching
- Tools
- VCenter On Demand
- VM Replication
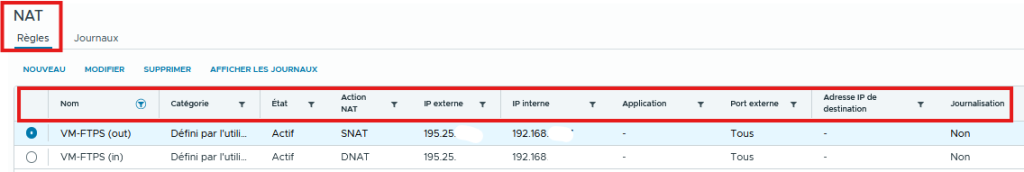
NAT Configure (NGP)
Overview
Note !
Your Edge gateway is the device that provides network filtering functionality. It is therefore on this gateway that you must create your DNAT and SNAT rules.
Here is a short explanation of their use :
| Rule | Common Name | Description |
| DNAT | Destination NAT | A DNAT rule is an incoming rule. It is used to route a packet arriving on a public interface from a certain IP or network to a VM on a private network. In practice the destination IP address of the packet will be replaced by another IP address. To illustrate, DNAT is used when communication is made FROM a Public network TO a Private network. |
| SNAT | Source NAT | An SNAT rule is an outgoing rule. It is used to route a packet arriving on a private interface from a certain private IP or a private network that wants to communicate with an external (Public) network. To illustrate, SNAT is used when communication is made FROM a Private network TO a Public network. |
NAT and Firewall rules combined can create confusion when we try to determine the correct IP address to which to apply the Firewall rule.
The diagram below summarizes the FW/NAT rule association.
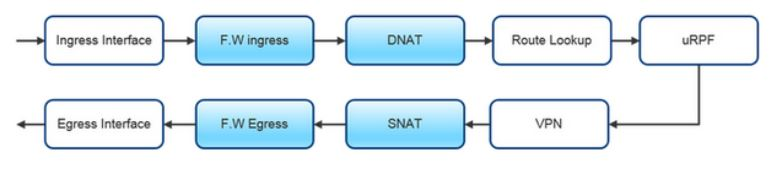
Managing NAT rules

Warning !
When you use DNAT, you can only perform 1 IP address / 1 NATed address translation. You are doing 1:1.
With SNAT, you can translate 1 IP address / 1 NATed address or one Subnet / 1 NATed address. You are doing 1:1 or n:1.
More details HERE
Access the Advanced Services of your T1 Edge from the Networking / Edge Gateways / NAT / NEW tab
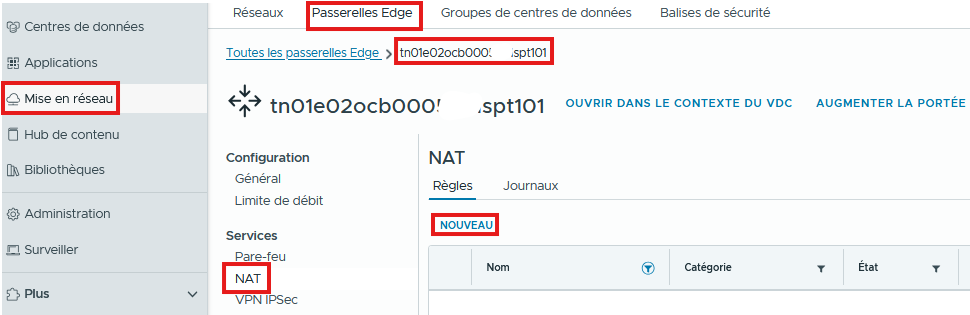
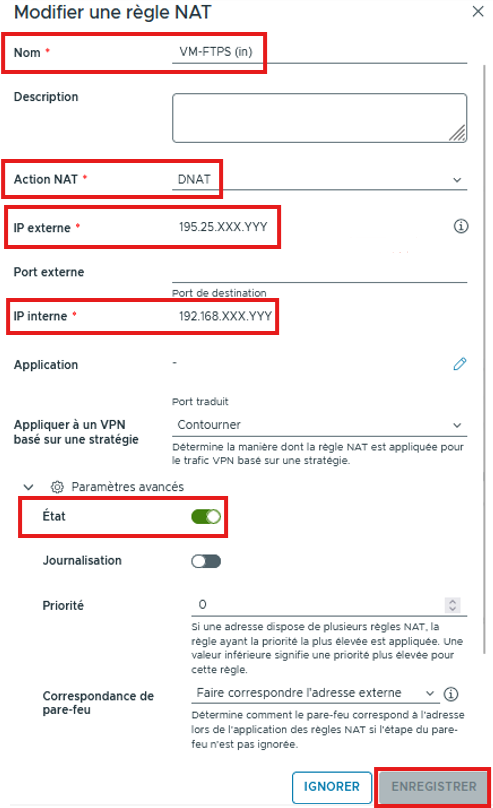
DNAT rule
- Name your rule
- Add a description if needed
- Choose DNAT
- Enter the External IP (Generally a public IP)
- Configure the External Port if needed
- Enter the Internal IP (Local – RFC 1918). This can also be a subnet.
- Define on which Port the rule will apply (Application), otherwise the rule will apply to all ports (any to any rule)
- Define the Priority of the rule (0 being the highest priority)
You can enable or disable the rule, enable logging, match the firewall to the External IP and SAVE
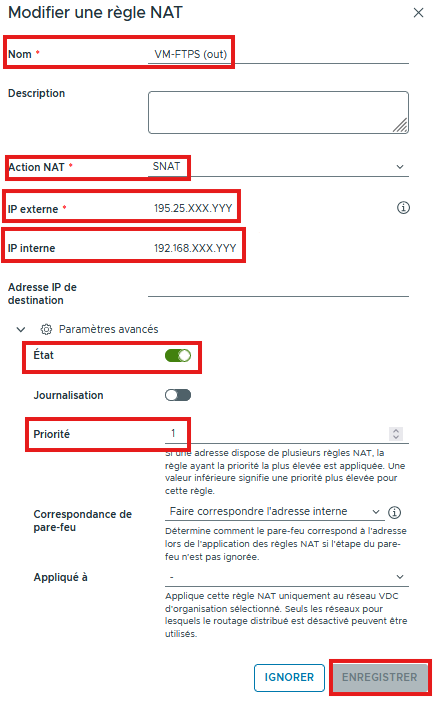
SNAT rule
- Name your rule
- Add a description if needed
- Choose SNAT
- Enter the External IP (Generally a public IP)
- Enter the Internal IP (Local – RFC 1918). This can also be a subnet.
- Enter a Destination IP address if needed (If the NAT should apply only for a specific destination).
- You can enable or disable the rule and logging
- Define the Priority of the rule (0 being the highest priority)
- You can match the firewall to the Internal IP