Network
Overview
The network and security layer of Cloud Avenue is provided by the NSX-T solution from vmware. The implementation is performed at two levels:
- a T0 Edge gateway, including a per-customer dedicated context, able to connect to the external networks: internet, BVPN Galery,Cross Connect, administration, etc. The T0 Edge gateway configuration is done automatically by the platform.
- a T1 Edge gateway, able to manage the vDC networks, whom configuration is done by the Customer from the vCloud Director portal.
The IP address ranges are chosen by the Customer, generally among non-routable subnets.
NSX-T gateways specifications
Depending on the needs, several configurations are available.
| Type of gateway | Class of service | Specifications |
Connected networks (recommandation) |
| T0 VRF | Standard | 300 Mbps max flow(*) |
|
| T0 VRF | Premium | 1 Gbps débit max (*) |
|
| Dedicated T0 | Medium | 3,5 Gbps max flow(*)
|
|
| Dedicated T0 | Large |
|
|
| T1 | Standard | 300 Mbps max flow (*)
|
A single interface for connection to the T0
|
| T1 | Premium | 1 Gbps max flow (*)
Need a T0 Premium |
|
| Dedicated T1 | Medium | 2,5 Gbps max flow (*)
Need a dedicated T0 |
|
| Dedicated T1 | Large | 6 Gbps max flow (*)
Need a dedicated T0 |
(*) The max flow means the global throughput available for the gateway.In software-defined networking environments, it is normal to observe a small difference between the bandwidth profile value and the throughput measured by end-to-end tools such as iPerf. This can be influenced by protocol/encapsulation overhead and traffic shaping behavior.
As an example, for a 300 Mbps profile, a measured TCP throughput around 270–290 Mbps may be within the expected range. In addition, TCP mechanisms (slow start / congestion window) and test conditions (test duration, number of streams, MTU) can impact the measured value.
All the gateways are in high availability mode by default. The max flow information is given according to a network packet size of 1500 bytes.
By default, the T0 VRF and T1 gateways are hosted on a mutualized cluster. It is possible to order a dedicated T0 & T1 (hosted on a dedicated VM cluster), for the following use cases:
- huge need of internet bandwidth
- organization with a lot of vDCs and several hundred VMs
- Customer preference for dedicated component (in addition to a dedicated cluster for example)
- need to manage a lot of T0 VRF
Upgrade
The transition from a standard T0 VRF gateway to a Premium T0 VRF or from a Premium T0 VRF gateway to a dedicated T0 requires planning and results in a service interruption.
The NSX configurations
General case
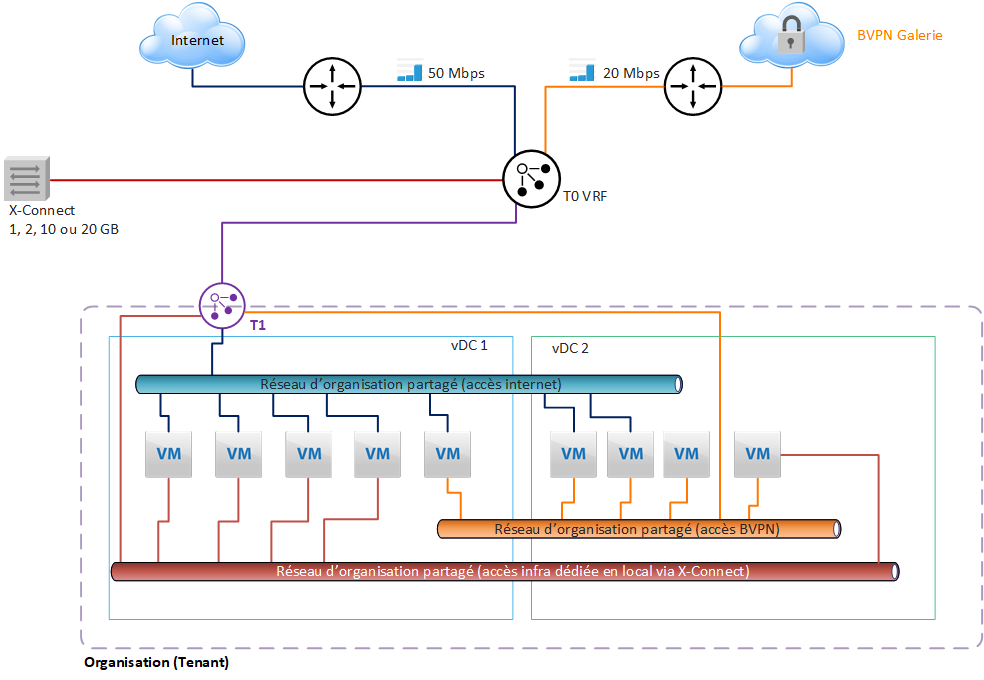
With this architecture, the Internet or VPN Gallery bandwidth subscribed by the Customer for each Organization is configured at the T0 level, and shared between the different vDCs.
A T1 gateway is used to create Organization networks that can be shared between all vDCs in the Organization.
Each T1 can be connected to a single T0 gateway, with a single interface.
In the diagram presented here, a T0 VRF gateway is subscribed by default and will manage all the underlying networks distributed by the T1 at the vDC level.
Internet bandwidth limitation
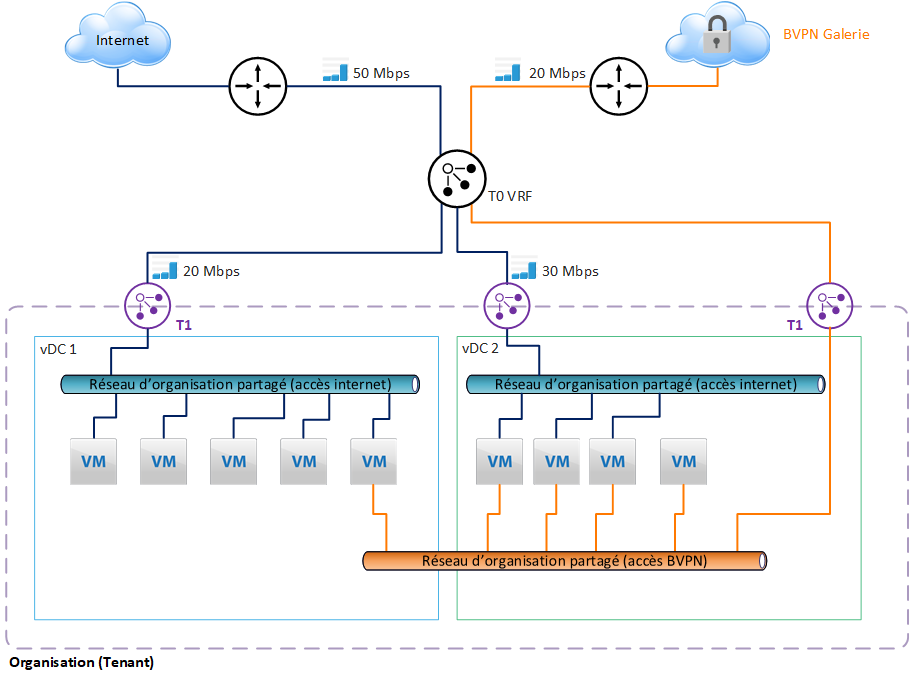
The Customer may limit the bandwidth of a T1 gateway. This makes it possible to control the sharing of bandwidth between the different vDCs.
Configuration with 2 T0 VRF
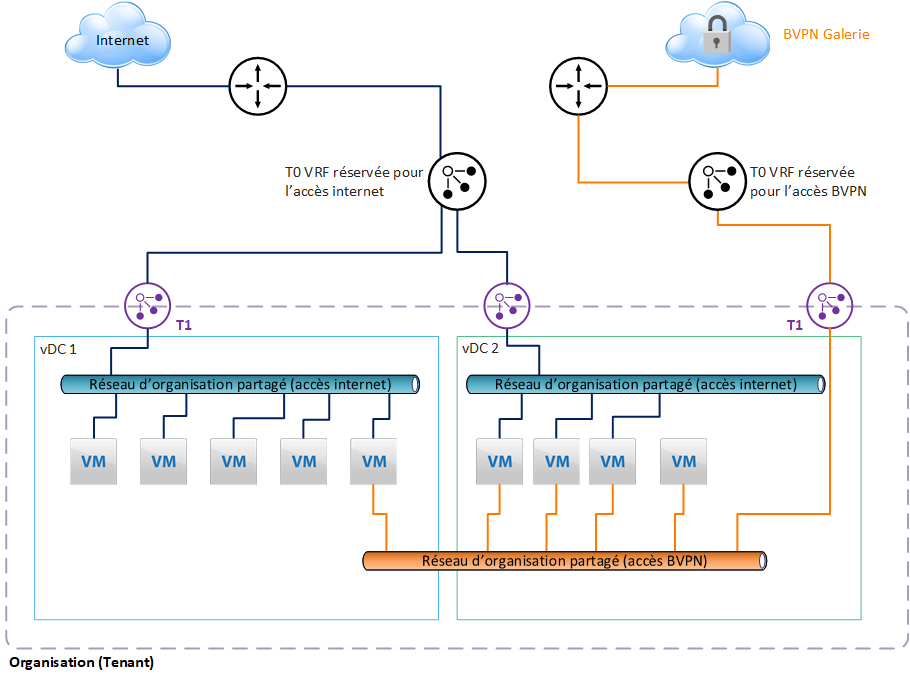
To meet internal security policy constraints, it is possible to separate the external networks and assign them a separate T0 VRF.
In our example, we have assigned a T0 VRF for internet access, and another T0 VRF for access to the BVPN Gallery.
This separation is recommended to avoid configuration errors made by the customer, which would lead to exposing networks or VMs on the internet that should not be exposed. Indeed, the configuration of each external network will be done in 2 different gateways in VCD.
Note that if the Customer needs to manage a lot of T0 VRF, he must consider the dedicated T0 option, which can provide up to 100 T0 VRF.
Integrated features
Organization networks
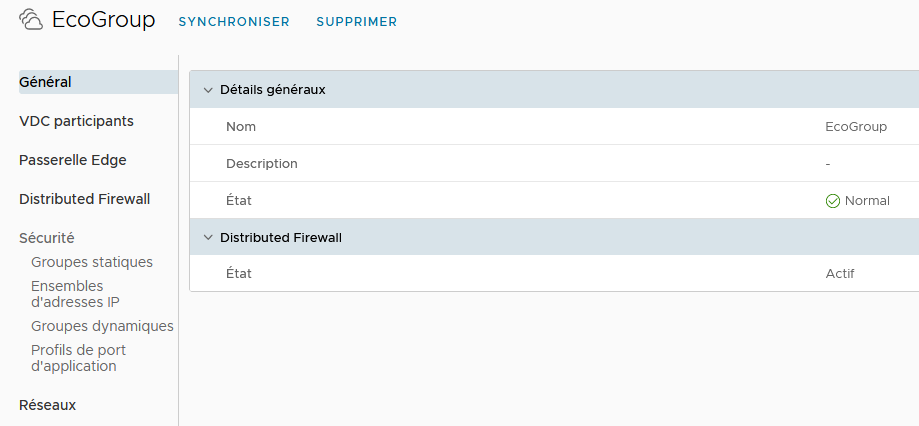
The Edge T1 gateway is used to create the internal networks of the vDC on which the VMs will be connected. The addressing of these networks is chosen by the Customer during configuration/creation. To share the networks between vDCs, it is necessary to create a group of vDCs, in order to include the vDCs concerned, which can then share the functionalities of the Edge gateway T1, and its networks.
Firewall
The T1 gateway offers a 2-level firewall:
- perimeter firewall, for north-south flows, i.e. entering and leaving the vDC (or group of vDCs)
- distributed firewall, for east-west flows, on a scope ranging from a single vDC to all the vDCs included in a group of vDCs.
Perimeter firewall configuration will be done in the Services options of the T1 Edge Gateway configuration. All incoming and outgoing flows of the vDC will be filtered through the rules implemented here. It will also be possible to configure a point-to-point IPSec VPN between the remote equipment and the Edge T1 gateway.
A Load Balancer is also available, providing basic functionality for clustering servers.
The Security option will allow you to manage part of the configuration related to the distributed firewall. This is where you need to define the security groups that carry the authorizations defined later in the firewall configuration (see below).
IP Address Management allows you to configure advanced T1 Edge Gateway IP services, such as DNS or DHCP forwardin
In the vDC group configuration, we will be able to configure the distributed firewall, and define fairly fine-grained permissions at the security group level.
This extremely powerful feature allows:
- effectively protect VMs by filtering east-west flows
- to create trust zones based on tags manually positioned on the VMs or built dynamically from programmed rules.
All features described below are configurable by Customer in the vCloud Director portal.
LBaaS ( Load Balancer as a Service)
All information related to Load Balancer are available here : LBaaS